Not knowing if what you’re experiencing is a heart attack or a heart burn can be extremely scary. The symptoms for both overlap to a good extent and can cause unnecessary worry and stress to the person experiencing a heart burn thinking they are having a heart attack. Which is why, we spoke to Dr. Sandesh Prabhu, Consultant – Cardiology and Electrophysiology, Manipal Hospitals Whitefield to explain us the difference between the two. He started off by explaining the two terms as below:
What is a heart attack?
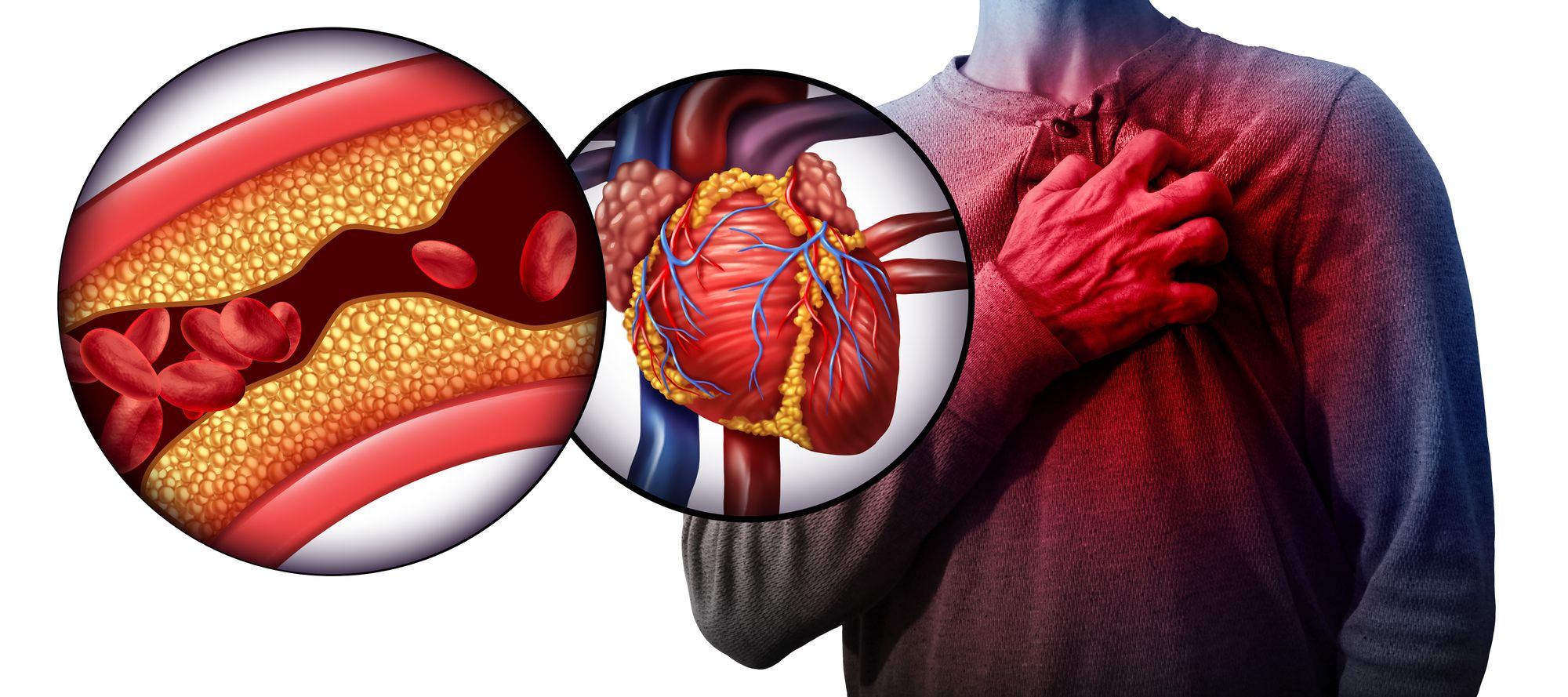
A heart attack (also called myocardial infarction) occurs when the coronary arteries (blood vessels supplying heart muscles) become narrow or are blocked due to the build-up of plaque (cholesterol deposits). This results in poor supply of blood to your heart, and can be responsible for the death of the heart tissues in the area where the blood vessels are affected.
What is a heartburn?
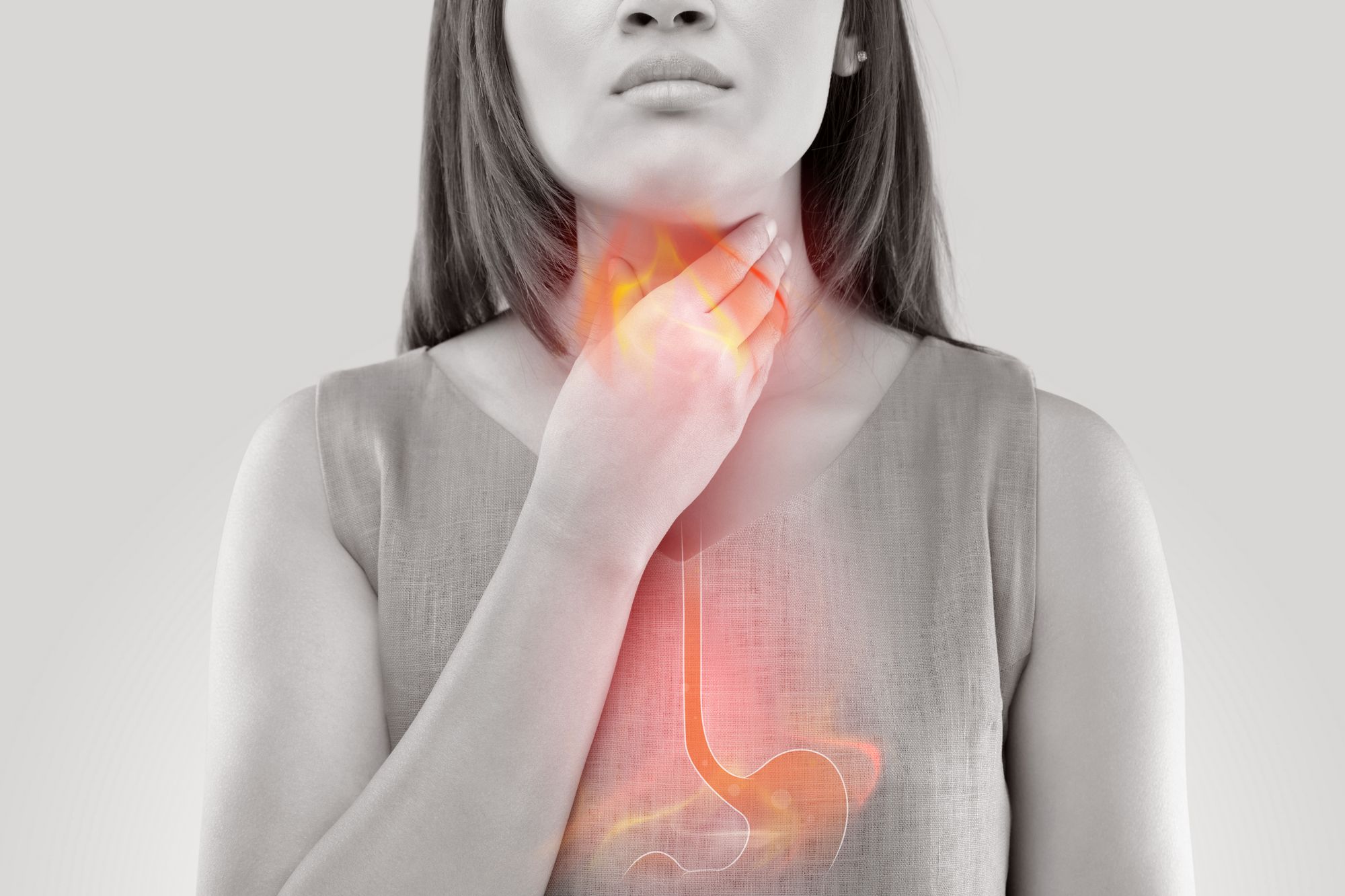
Heartburn is a symptom of acid reflux. Acid reflux occurs when acid from your stomach backs up into your oesophagus causing a burning sensation in the chest (behind the breastbone). Heartburn is often experienced after having a heavy meal.
Is that chest pain because of heartburn or a heart attack?
Identifying the difference between heartburn and heart attack may be a bit difficult because their symptoms usually overlap. However, the most important difference is that:
1. For HeartBurn
The pain in your chest is usually heartburn if you experience radiating pain throughout the entire chest and the pain spreads towards your neck, throat, or jaw. It usually develops a few hours after a heavy meal.
2. For Heart Attack
It is most probably a heart attack if your chest pain occurs suddenly. It is important to look beyond the chest pain symptoms to understand if you are experiencing a heart attack. The other symptoms that you should watch out for include:
- Getting extremely tired
- Heaviness in your chest
- Profuse sweating or cold sweat
- Shortness of breath that eases with rest
- Radiating pain that often starts in your chest and spreads to your jaw, back or arms
- Nausea
- Vomitting
- Light-headedness or dizziness
- Confusion
Though a heart attack can occur to anyone, the risk is higher in certain populations, including those with:
- Obesity
- Smoking
- History of heart problems or risk factors of diabetes, hypertension, high cholesterol, etc.
- Previous history of heart attacks
- Family history of heart attacks
- Stress or sleep disorders
In such cases, it is best to seek immediate medical attention even if you have the slightest pain or discomfort in your chest.

Similarities & Differences Between Symptoms Of Heartburn & Heart Attack
Common Symptoms Between Heartburn & Heart Attack
- Chest pain
- Burning sensation in the chest
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Indigestion
Differences Between Heartburn & Heart Attack
- Heartburn is a symptom of acid reflux whereas a heart attack occurs when the coronary arteries are blocked due to the build-up of plaque, resulting in poor blood circulation to the heart.
- A heartburn usually occurs after a heavy meal but a heart attack can occur at any time suddenly.
- The former can cause an uncomfortable burning sensation in your throat, accompanied by a sour, or acidic taste in the back of your throat or pain that worsens with bending or when lying down. But the typical signs and symptoms of the latter include tightness or pain in your chest that may radiate to your neck, jaw or back accompanied by cold sweat, fatigue, sudden dizziness, etc.
- When experiencing a heartburn, the chest pain or discomfort usually subsides after taking antacids but if its a heart attack, the chest pain usually does not subside after taking antacids.
- Heartburns are not life threatening whereas a heart attack can be fatal and needs immediate medical attention.

When should you see a doctor for heartburn?
Heartburn is common and is usually treated by avoiding triggers of heartburn, with home remedies, or with over-the-counter medications like antacids or acid blockers. However, severe, and frequent heartburn episodes can sometimes cause serious health issues like inflammation of the oesophagus, gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), respiratory problems, persistent cough, and Barrett’s oesophagus (which may lead to oesophagul cancer).
Consult your doctor if:
- Your heartburn is severe
- You find it hard to swallow
- You are losing weight without even trying
- Your heartburn is persistent despite taking antacids for more than two weeks or longer
- Your heartburn or chest discomfort interferes with your regular activities.
Cardiac Vs. Non-Cardiac Chest Pain
Cardiac chest pain is associated with pain caused by heart diseases such as:
- Heart attack
- Atherosclerosis
- Coronary heart disease
Non-cardiac chest pain is associated with pain caused by non-cardiac issues like:
- Problems of the oesophagus (such as gastroesophageal reflux disease, oesophageal motility disorders, etc)
- Lung conditions
- Stomach problems
- Psychiatric problems like stress, anxiety, and depression

How do different gastrointestinal issues affect your heart?
Gastrointestinal issues that indicate a heart condition (i.e. cardiovascular disease) include:
- Intestinal ischemia: Clogged gut arteries due to build-up of plaque.
- Chronic atrial and intestinal dysrhythmia (CAID) is a disorder that impairs the peristalsis (rhythmic muscle contractions) that moves food through the intestines causing intestinal pseudo-obstruction.
- Changes or alterations in the gut microbial community have been linked with the progression of atherosclerosis, heart failure, and other cardiovascular diseases.
- A muscle spasm in your oesophagus or pain in the gall bladder can cause chest pain similar to that of a heart attack.
- Epigastric pain is defined as pain or discomfort in the upper abdomen. Though epigastric pain can be caused by conditions related to digestion, such as peptic ulcer disease, gastritis, acid reflux etc, it can also be a symptom of an impending heart attack. Evidence suggests unexplained chest/epigastric pain in patients with normal endoscopy is a strong predictor of heart attacks and increases mortality.
Differential Diagnosis
To diagnose heartburn, your doctor may recommend:
- Endoscopy, to check for abnormalities in your oesophagus and to extract tissue samples (biopsy) from your oesophagus for further analysis.
- Ambulatory acid probe tests to identify acid reflux.
- Oesophageal motility testing, to measure movement and pressure in your oesphagus.
To diagnose a heart attack, your doctor will take a complete family history and your complete physical examination to assess the risk factors of a heart attack. He or she will order tests such as:
- Electrocardiogram (ECG)
- Blood tests
- Echocardiogram
- Coronary catheterization (angiogram)
Conclusion
Chest pain with or without epigastric pain is a common symptom of both heartburn and heart attacks and may pose a challenge for a patient to differentiate them and seek medical help. Though heartburns are relatively harmless, heart attacks can be fatal and need immediate medical attention. Patients are advised to visit the hospital without any delay in case of doubt to enable appropriate diagnosis and management.
Join the Girl Tribe by MissMalini to be a part of more such conversations. Explore the app!

