Anaemia is of the most pressing concerns of health care practitioners all over the world. The cases of anaemia have been multiplying rapidly owing to additional lifestyle and stress-related disorders. Young children, women and people with long term diseases are more susceptible to anaemia. In women, anaemia is generally caused due to loss of blood during periods or pregnancy. As per the recent global statistics from the World Health Organization (WHO), 40% of women and 42% of children under the age of 5 are anaemic.
What Is Anaemia
A good flow of oxygen to every body organ helps to maintain good health and better healing. When the body does not get enough oxygen due to the lack or impairment of the oxygen-carrying Red Blood Cells (RBC), the body is anaemic. The heart needs to pump harder to get enough oxygen to the body causing stress and fatigue. Anaemia causes the haemoglobin or hematocrit levels to drop dramatically with time. The optimal haemoglobin levels in a human being vary with factors like sex, age and lifestyle.
Types Of Anaemia
There over 400 types of anaemia which are broadly classified in three major categories- due to loss of blood, decrease or impairment of RBCs and spoliation of RBCs. Globally, the most common cause is due to deficiencies and chronic infectious diseases.
Symptoms Of Anaemia
The symptoms of anaemia are shortness of breath, constant body ache, intense fatigue and weakness. It also causes unusual rapid heartbeats, cold hands or feet and pale skin. Anaemia may cause pica, ulcers and insomnia. The symptoms also vary with the type of anaemia the person is subjected to.
Testing And Treating Anaemia
While testing for anaemia, your physician will consider family history, bad habits like cigarette smoking or alcohol addiction, blood test reports that include complete blood counts and deficiency checks for vital aspects like vitamins and minerals. Depending on the cause, type and intensity of the disorder, a suitable treatment is prescribed.
Treating severe cases include blood transfusions or bone marrow transplants, administration of cancer drugs like Droxia or Hydrea, blood filtering and oxygen therapies. It also includes treating the underlying chronic diseases causing low haemoglobin. General cases include treating iron deficiencies via suitable supplements, B-12 shots and folic acid supplements
Preventing Anaemia
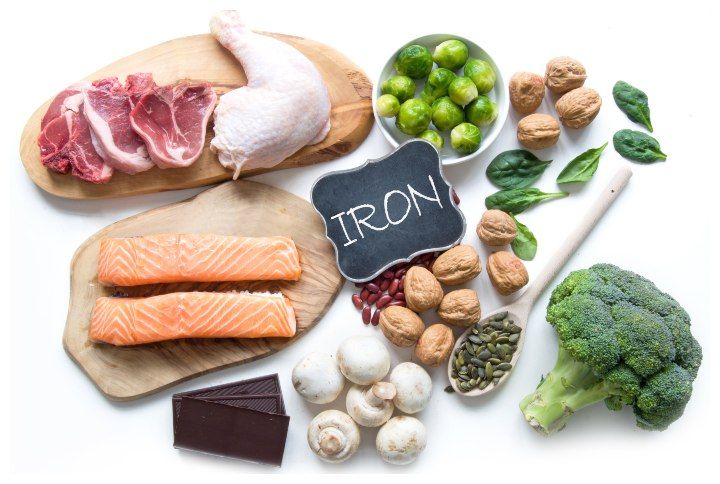

Prevention of anaemia is easy and in sync with a good lifestyle. Healthcare basics like a good diet, hydration and ample exercise play a crucial role. Exercise helps beat the condition by balancing hormones and increasing the absorption of nutrients from food. It also helps detoxify and boost blood circulation, thus providing the body organs with ample oxygen.
A good diet is a key to prevent and cure anaemia to a great level too. Kitchen cures are for real. Red meat, poultry, fish, dark leafy vegetables and eggs are great sources of iron and nutrients essential to boost the production of RBCs. Other than these, including fresh fruits, nuts, tofu and dark chocolate can help increase the haemoglobin too.
If you are experiencing the symptoms of anaemia, please consult your physician before adopting any form of treatment.
For more updates like these, join Malini’s Girl Tribe on Facebook & Instagram!